Appendixes
Appendix A: Commodity Exchange Operating System, 1969
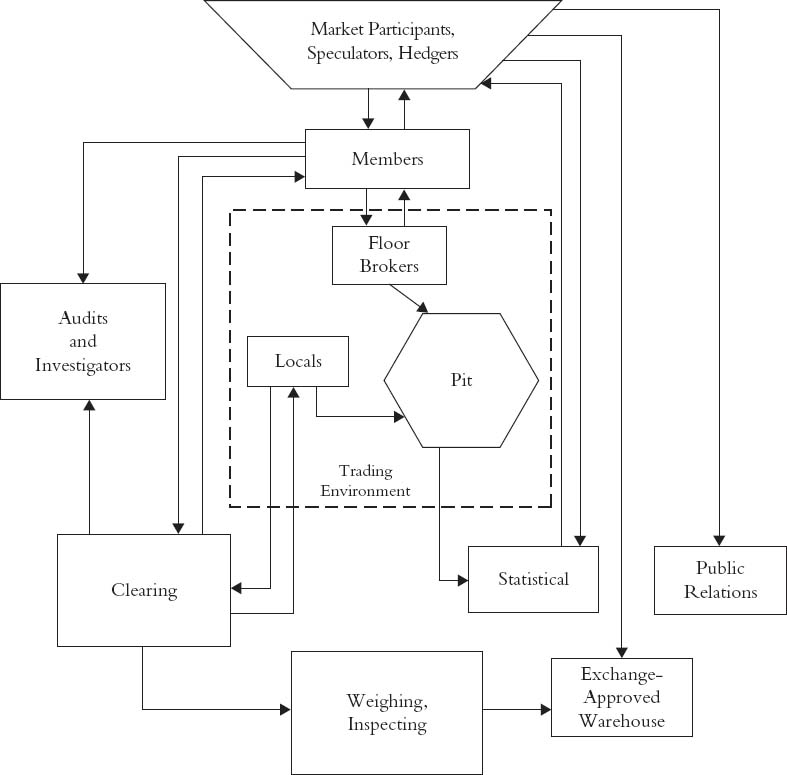
This Appendix describes the operating system of commodity exchanges that existed in 1969. The system is triggered by (1) a decision to buy or sell by a speculator or hedger or (2) customer intention to deliver. The schematic representation indicates that orders from speculators and hedgers are sent to members of the exchange. These orders are then transmitted to the trading floor to be matched in an area called the ring or pit, a name evocative of the unique architecture of trading floors at the Chicago Board of Trade.1 The diagram also contains a unit labeled “Locals,” an alternative term for floor traders. After a trade is consummated by either a broker or a principal (speculator or hedger) trading for their own account, it is recorded on an order or trading card. Trading cards and orders are put on the computers of the clearing members, who provide the information to the clearinghouse.
Appendix B: GNMA Advisory Committee
Anaheim Savings
Bache & Co.
Bank of America
Brentwood Mortgage Corp.
Citizens Savings & Loan Association
CMI
Engel Mortgage Company
The First Boston Corporation
First Federal Savings and Loan Association of Miami
GNMA
Great Western Savings & Loan Association
Hornblower & Weeks-Hemphill, Noyes
Huntoon, Paige & Co., Inc.
Kaufman and Broad, Inc.
R.H. Lapin & Co.
Mortgage Guaranty Insurance Corporation ...
Get Good Derivatives: A Story of Financial and Environmental Innovation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

