Chapter 2. The mobile radio channel and the cellular principle
Many measures, functions and protocols in digital mobile radio networks are based on the properties of the radio channel and its specific qualities, in contrast to information transmission through guided media. For the understanding of digital mobile radio networks it is therefore helpful to know a few related basic principles. For this reason, the most important fundamentals of the radio channel and of cellular and transmission technology are presented and briefly explained in the following. For a more detailed treatment, see, for example, Bertsekas and Gallager (1987), Lee (1989), Proakis (1995) and Steele and Hanzo (1999).
Characteristics of the mobile radio channel
The electromagnetic wave of the radio signal propagates under ideal conditions in free space in a radial-symmetric pattern. The received power Pr decreases with the square of the distance L from the transmitter. Specifically, the received power Pr can be described according to the free-space model as a function of the transmit power Pt, the distance L and the wavelength of the radio signal λ as
Equation 2.1.
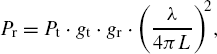
where gt and gr are the transmit and receive antenna gains, respectively. While this model is appropriate, for instance, for inter-satellite as well as for Earth-to-satellite communication, it does not capture the effects of terrestrial radio propagation, ...
Get GSM - Architecture, Protocols and Services, Third Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

