50 IBM Enterprise Workload Manager
These numbers can be changed if needed. However, if limits are made too small,
applications may start getting failure return codes. If you make them too large, you run the
risk of the system failing by running out of heap space. If you make the completion buffer size
too small, the EWLM agent may not see all completed transactions. If you change the priority
of the managed server to a high number, the managed server may not run often enough. If
you choose this number to be too small this may prevent critical system daemons from
running. We therefore advise you to work with default numbers to start with and to change
them only if you run into problems.
Verify managed servers status from Control Center
The configuration of our domain manager running on Linux is complete, as is the
configuration of all managed servers in our environment running on AIX and Windows. When
we go back to the EWLM Control Center and look at the status of the managed servers we
should be able to see all four machines now. We open a browser with the following URL:
http://ewlmdm1.itso.ibm.com®:20003/webui
We log in to the EWLM Control Center with any of the mapped users, which in our setup are
ewlmadm, ewlmops and ewlmmon. The available options will be different for these user roles but
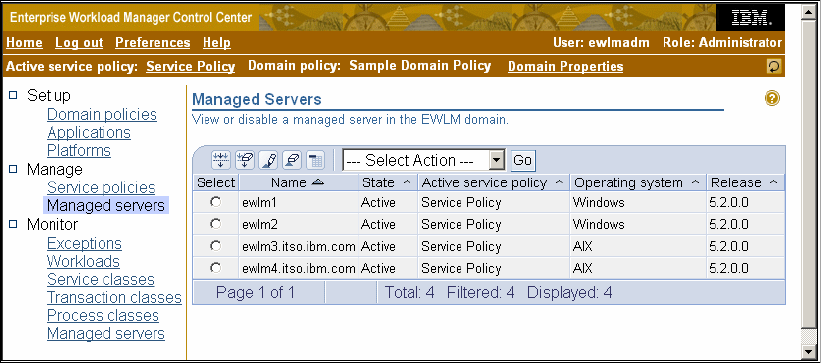
all three can do monitoring tasks. When we click on managed servers on the left menu bar we
see the output shown in Figure 2-22. This shows that all four systems are active. It provides
information on the operating system and its version, where Windows release 5.2 corresponds
to Windows 2003 and Windows release 5.0 corresponds to Windows 2000.
Figure 2-22 Monitoring status of managed servers after initial configuration
We are now ready to start instrumenting our applications. This is described in Chapter 3,
“Enabling middleware for EWLM” on page 57. If your domain manager or managed servers
run on supported operating systems other than the ones we described for our test setup, refer
the Section 2.5, “Installing the domain manager on other operating systems” and 2.6,
“Configuring managed servers on other operating systems” on page 54. We will not go
through the installation and configuration steps in detail but outline the procedure highlighting
any differences you may see.
2.5 Installing the domain manager on other operating systems
In the previous section we guided you through the installation of the domain manager on a
Linux platform. These steps are valid in general. Nonetheless, there are some differences
Get IBM Enterprise Workload Manager Release 1 now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

