24.5 Discriminant Analysis
The aim of cluster analysis is to group observations, or variables, into initially unknown groups of similar elements. Unlike that, discriminant analysis is applied if the group each observation belongs to is known and one is interested in knowing how the available variables affect the classification, in order to be able to classify a new observation whose variable values are known but not the group it belongs to.
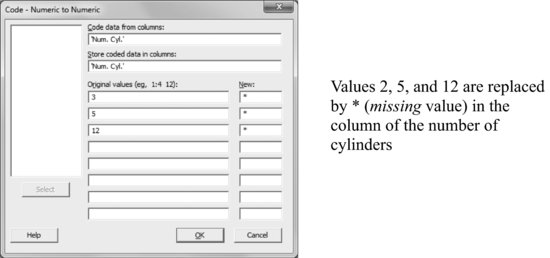
We continue working with the CARS.MTW file. Now, we will use the first 150 cars to establish the number of cylinders allocation criterion as a function of the remaining variables. There are cars with 3, 4, 5, 6, 8 and 12 cylinders but to facilitate the analysis consider only those with 4, 6, and 8 cylinders.
Data > Code > Numeric to Numeric
Data > Subset worksheet
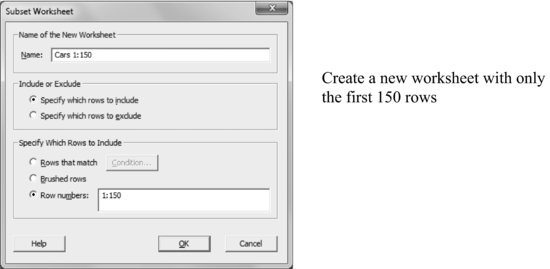
Using this new worksheet, with the cars from rows 1 to 150, perform a discriminant analysis.
Stat > Multivariate > Discriminant Analysis
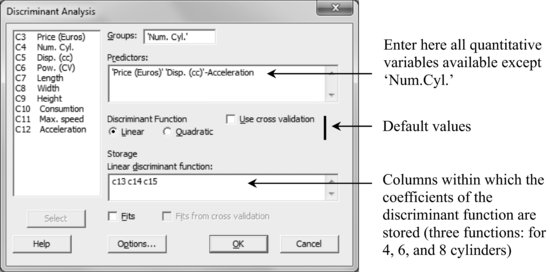
In addition to the descriptive information on the data, in the Session Window a summary of the allocations made, the discriminant function for each group and a summary of the errors done appear.
We can use the discriminant functions to assign ...
Get Industrial Statistics with Minitab now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

