CHAPTER 16 Dilutive Securities and Earnings per Share
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
After studying this chapter, you should be able to:
- Describe the accounting for the issuance, conversion, and retirement of convertible securities.
- Explain the accounting for convertible preferred stock.
- Contrast the accounting for stock warrants and for stock warrants issued with other securities.
- Describe the accounting for stock compensation plans.
- Discuss the controversy involving stock compensation plans.
- Compute earnings per share in a simple capital structure.
- Compute earnings per share in a complex capital structure.
Kicking the Habit
Some habits die hard. Take stock options—called by some “the crack cocaine of incentives.” Stock options are a form of compensation that gives key employees the choice to purchase shares at a given (usually lower-than-market) price. For many years, companies were hooked on these products. Why? The combination of a hot equity market and favorable accounting treatment made stock options the incentive of choice. They were compensation with no expense to the companies that granted them, and they were popular with key employees, so companies granted them with abandon. However, the accounting rules that took effect in 2005 required expensing the fair value of stock options. This new treatment has made it easier for companies to kick this habit.
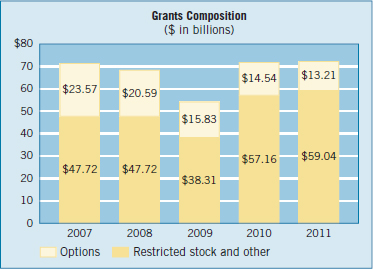
As shown in the chart above, ...
Get Intermediate Accounting, 15th Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

