3THE ELEMENTS OF DIGITAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
This chapter briefly covers some general topics on digital signal transmission and detection theory. The reader may refer Refs. [1–10]for more comprehensive details.
Figure 3.1 shows the block diagram of a baseband digital transmission system. The transmitted binary data symbols are applied at the pulse repetition frequency to an encoding circuit that performs logical manipulations such as differential encoding and two-to-multilevel conversion. Corresponding to the logical data symbols, the pulse-shaping circuit sends out digitally encoded waveforms into the channel. Pulse shaping is intended to get a narrower signal spectrum or to match the spectrum to the transfer characteristics of the channel, for example, a dc blocked channel. The manipulation of data by the encoder or pulse-shaping circuits is called line coding. The transmitted signal is detected at the receiver. Typically, the transmitted signal is corrupted by noise and interference in the channel. The detection process includes noise band limitation and decision-making on the digital signal. Achieving a lower error rate for the decisions is the main concern in the receiver. The determined logical symbol is decoded appropriately corresponding to the encoding.
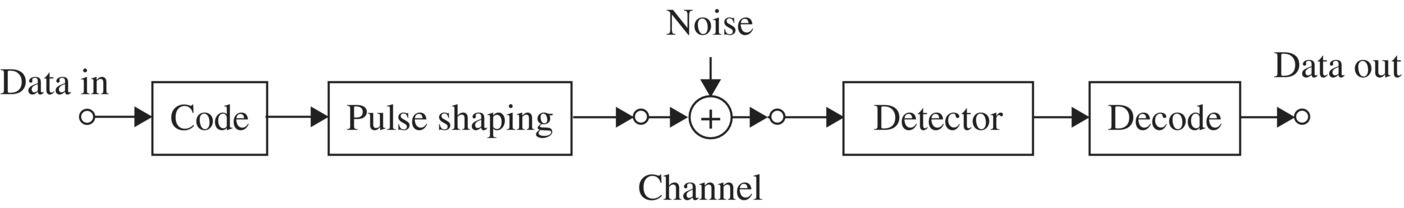
FIGURE 3.1 Digital transmission system.
3.1 PULSE SHAPING
Pulse shaping with limited bandwidth results in an impulse ...
Get Introduction to Digital Mobile Communication, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

