Chapter 10
Ethernet Technology – Fault Management
10.1. Introduction
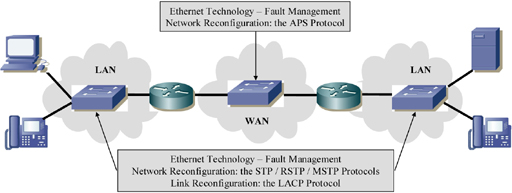
Fault management concerns the reconfiguration of the Ethernet network in instances of node (switch) loss, and the reconfiguration of an aggregate link when failure in one of the links making up the assembly occurs (Figure 10.1).
The switches in the Ethernet network exchange messages corresponding to the STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) in order to create a spanning tree that removes transmission loops in the Ethernet network. This protocol also enables the reconfiguration of the spanning tree in instances where faults occur at a network link or node.
The RSTP (Rapid STP) is an extension of the STP, improving the latter’s reconfiguration time in case of topology change.
The MSTP (Multiple STP) allows for the creation of several spanning trees based on constructed VLANs and complements the STP or the RSTP. It brings a load-balancing function to the network, which is obtained by constructing separate spanning trees.
It is possible to connect two switches with several links, thus creating an aggregate. This arrangement enables an increase in the rate between the two switches. The LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) allows the creation of such an aggregate and its reconfiguration if one of the links fails.
Figure 10.1. Ethernet technology – fault management
The aggregation network can employ Ethernet technology according ...
Get IP, Ethernet and MPLS Networks: Resource and Fault Management now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

