6.4. Polymorphism
Class inheritance is not just about reusing classes that you have already defined as a basis for defining a new class. It also adds enormous flexibility to the way in which you can program your applications, with a mechanism called polymorphism. So what is polymorphism?
The word polymorphism generally means the ability to assume several different forms or shapes. In programming terms it means the ability of a single variable of a given type to be used to reference objects of different types and to automatically call the method that is specific to the type of object the variable references. This enables a single method call to behave differently, depending on the type of the object to which the call applies. This is illustrated in Figure 6-4.
Figure 6.4. Figure 6-4
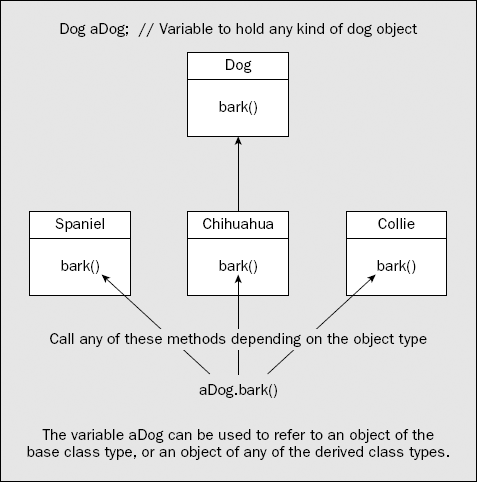
A few requirements must be fulfilled to get polymorphic behavior, so let's step through them.
First of all, polymorphism works with derived class objects. It also depends on a new capability that is possible within a class hierarchy that you haven't met before. Up to now you have always been using a variable of a given type to reference objects of the same type. Derived classes introduce some new flexibility in this. Of course, you can store a reference to a derived class object in a variable of the derived class type, but you can also store it in a variable of any direct or indirect base class type. ...
Get Ivor Horton's Beginning Java™ 2, JDK™ 5th Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

