Elements
Let's look more closely at the elements that make up regular expressions.
Regexp Choice
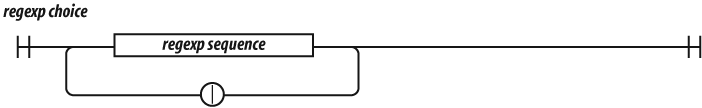
A regexp choice contains one or more regexp
sequences. The sequences are separated by the | (vertical bar) character. The choice matches if
any of the sequences match. It attempts to match each of the sequences in order.
So:
"into".match(/in|int/)
matches the in in into. It wouldn't match int
because the match of in was
successful.
Regexp Sequence

A regexp sequence contains one or more regexp factors. Each factor can optionally be followed by a quantifier that determines how many times the factor is allowed to appear. If there is no quantifier, then the factor will be matched one time.
Regexp Factor

A regexp factor can be a character, a parenthesized group, a character class, or an escape sequence. All characters are treated literally except for the control characters and the special characters:
\ / [ ] ( ) { } ? + * | . ^ $which must be escaped with a \ prefix if
they are to be matched literally. When in doubt, any special character can be
given a \ prefix to make it literal. The
\ prefix does not
make letters or digits literal.
An unescaped . matches any character except
a line-ending character.