Addressing and Connections Identification
In IEEE 802.16-2009, IEEE 802.16j-2009 and IEEE 802.16m, air interfaces are identified for the different elements (BS SS, RS, and MS) by a unique and universal 48-bit MAC address. This address is not used for identifying the MAC data PDU as in other IEEE 802.x technologies; rather, it is used during the initial ranging and authentication process. The standard also defines logical identifiers to facilitate data and control operations in the different operational modes (PMP, MR).
Logical Identifiers in IEEE 802.16-2009
A connection-oriented technology, IEEE 802.16 establishes a logical link between the BS and MS MAC layers that is identified by a 16-bit unidirectional Connection Identifier (CID). The CID is used in the MAC PDU header as a temporary address for the data transmission. Three types of management connections are defined:
- Basic: A mandatory connection established during initial ranging to exchange short, time-urgent MAC management messages;
- Primary: A mandatory connection established to exchange longer, more delay-tolerant MAC management messages; and
- Secondary: An optional connection to transfer delay-tolerant, standards-based messages such as Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), and Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) messages.
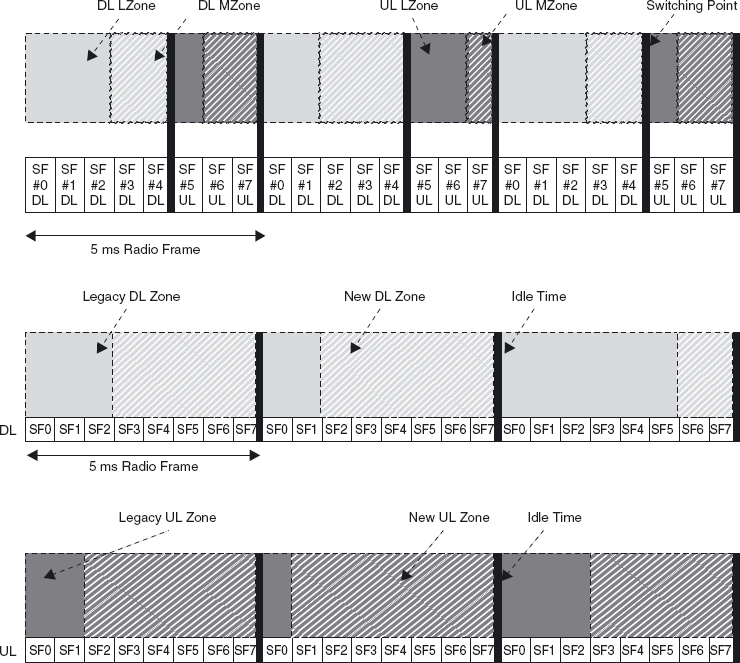
Figure 4.9 Example of Time zones in TDD and FDD ...
Get LTE, LTE-Advanced and WiMAX: Towards IMT-Advanced Networks now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

