In a supervised learning problem, there will always be a dataset, defined as a finite set of real vectors with m features each:
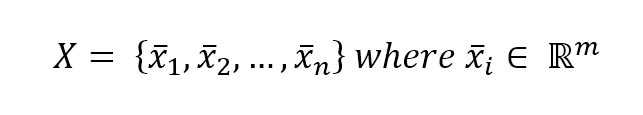
Considering that our approach is always probabilistic, we need to consider each X as drawn from a statistical multivariate distribution D. For our purposes, it's also useful to add a very important condition upon the whole dataset X: we expect all samples to be independent and identically distributed (i.i.d). This means all variables belong to the same distribution D, and considering an arbitrary subset of m values, it happens that:
The corresponding output values can be both numerical-continuous or ...

