Let's consider a small dataset built by adding some uniform noise to the points belonging to a segment bounded between -6 and 6. The original equation is y = x + 2 + η, where η is a noise term.
In the following graph, there's a plot with a candidate regression function:
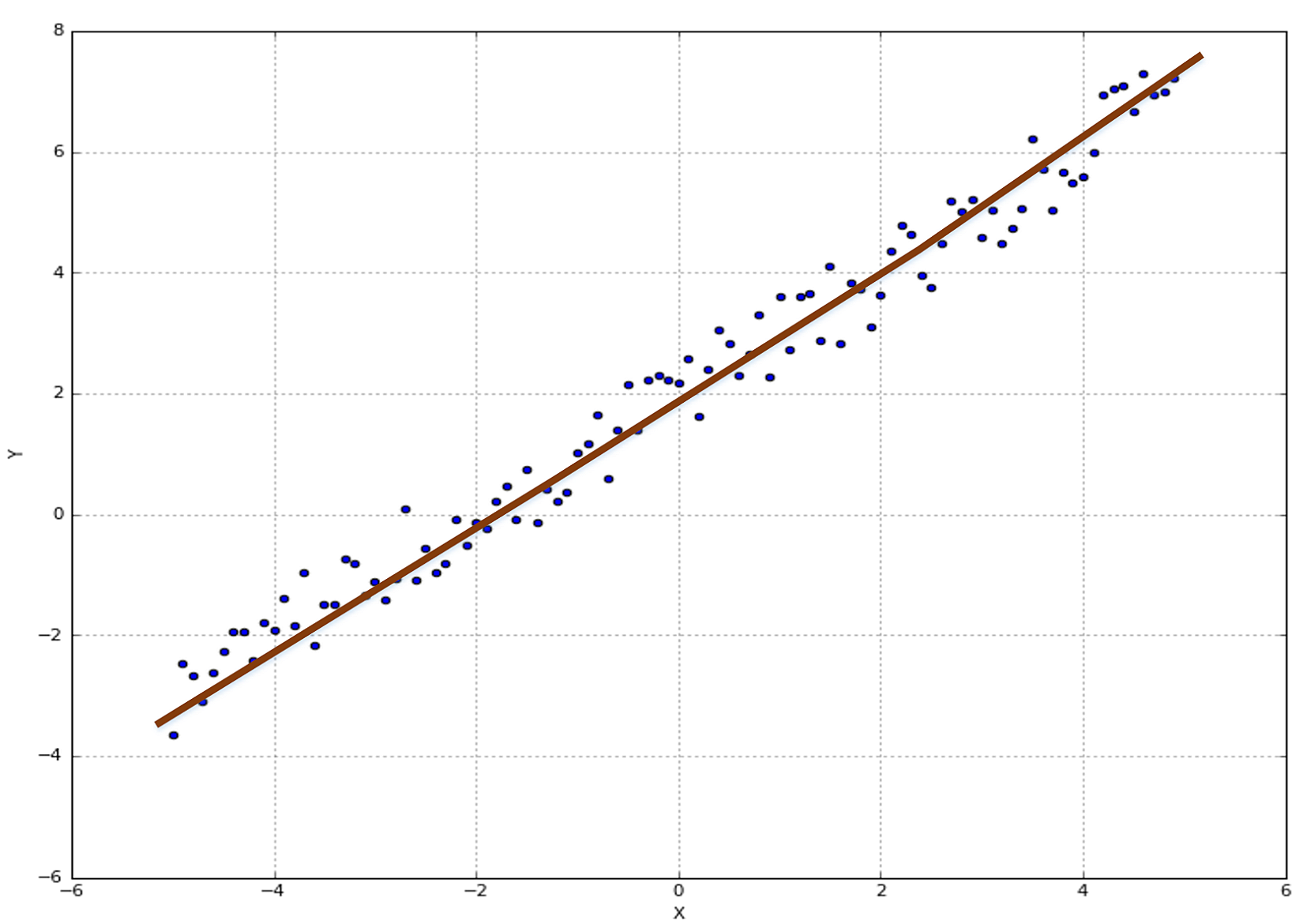
The dataset is defined as follows:
import numpy as npnb_samples = 200X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.05)Y = X + 2Y += np.random.normal(0.0, 0.5, size=nb_samples)
As we're working on a plane, the regressor we're looking for is a function of only two parameters (the intercept and the only multiplicative ...

