We can implement the algorithm in Python, using a test bidimensional dataset:
from sklearn.datasets import make_classificationnb_samples = 100nb_unlabeled = 75X, Y = make_classification(n_samples=nb_samples, n_features=2, n_informative=2, n_redundant=0, random_state=1000)Y[Y==0] = -1Y[nb_samples - nb_unlabeled:nb_samples] = 0
As in the other examples, we set y = 0 for all unlabeled samples (75 out of 100). The corresponding plot is shown in the following graph:
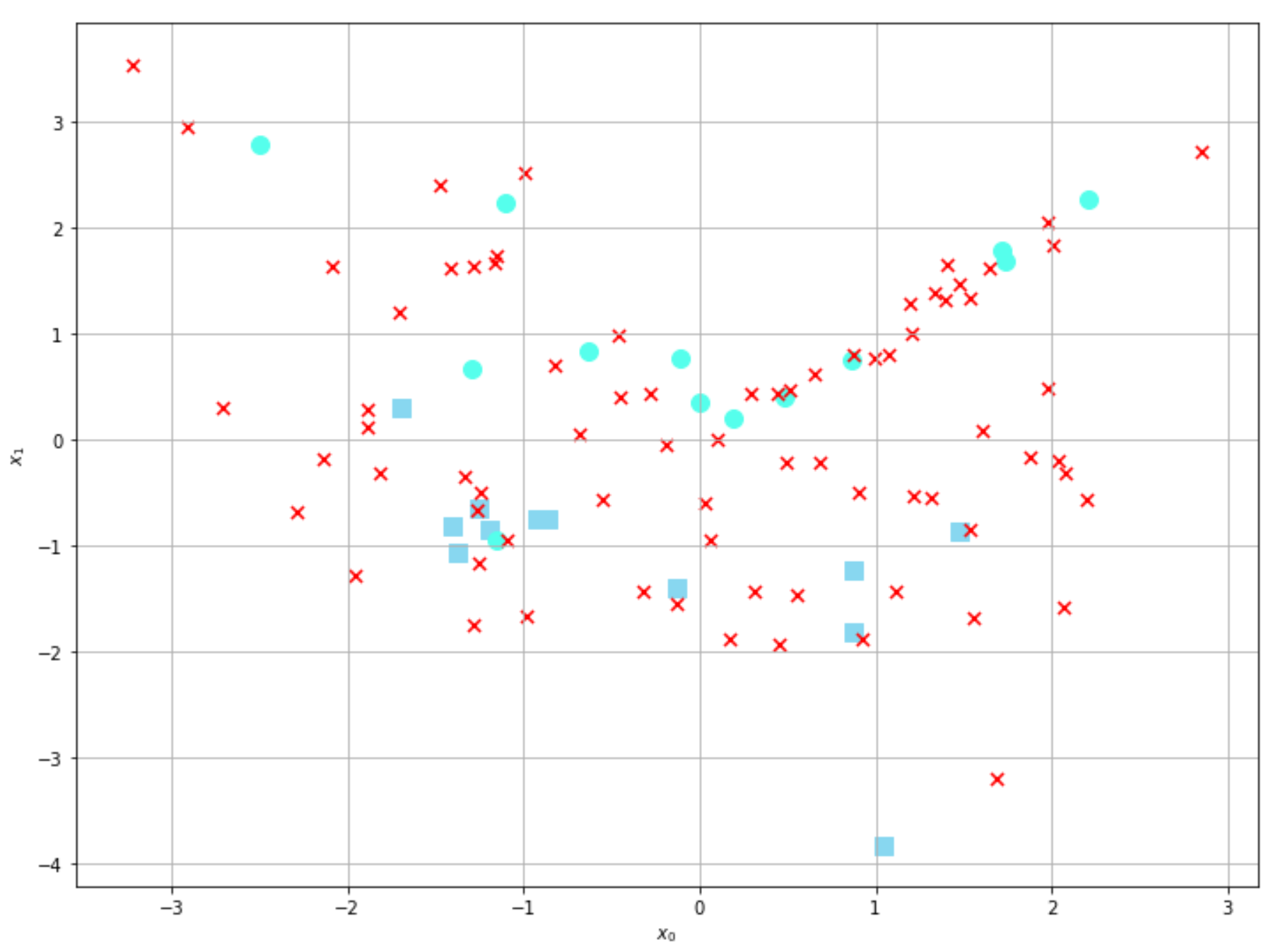
The dots marked with a cross are unlabeled. At this point, we can define the affinity matrix. In this case, we compute it using ...

