Preface
This work explains the evolutions of architecture for mobiles and summarizes the different technologies:
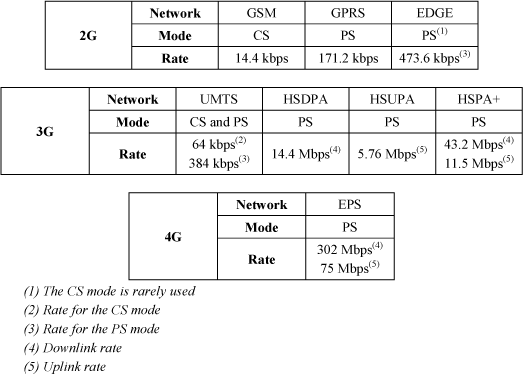
– 2G: the GSM (Global System for Mobile) network, the GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) network and the EDGE (Enhanced Data for Global Evolution) evolution;
– 3G: the UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) network and the HSPA (High Speed Packet Access) evolutions:
– 4G: the EPS (Evolved Packet System) network.
The telephone service and data transmission are the two main services provided by these networks. The evolutions are fundamentally dictated by the increase in the rate of data transmission across the radio interface between the network and mobiles.
The services are implemented according to two modes:
– the CS (Circuit Service) mode. This mode is characterized by the allocation of a resource dedicated to a flow. This mode provides both types of service;
– the PS (Packet Service) mode. This mode is characterized by the allocation of a resource shared by several flows. This mode is solely used for data transmission.
Table 1. Mobile networks – rates
The network architecture for mobiles reveals two subsystems:
– the AN (Access Network). This sub-system can be used to allocate the radio resource to the mobile, so that it can either be dedicated or shared. ...
Get Mobile Networks Architecture now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

