- Read in the names dataset, and output it:
>>> names = pd.read_csv('data/names.csv')>>> names
- Let's create a list that contains some new data and use the .loc indexer to set a single row label equal to this new data:
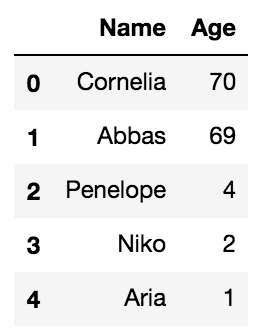
>>> new_data_list = ['Aria', 1]>>> names.loc[4] = new_data_list>>> names
- The .loc indexer uses labels to refer to the rows. In this case, the row labels exactly match the integer location. It is possible to append more rows with non-integer labels:
>>> names.loc['five'] = ['Zach', 3]>>> names
- To be more explicit ...