2Control of induction machines
Fernando Briz and Gonzalo Abad
2.1 Introduction
Induction machines can be considered as the workhorse of industry, as they are rugged and cheap. Before the advent of electronic power converters the use of induction machines was limited to applications operating at nearly constant speed. The advances in the field of power semiconductors, combined with the development of powerful and cheap digital signal processors and adequate control strategies, have resulted in the widespread industrial use of AC variable speed drives (VSDs). VSDs using three‐phase induction motors can be found nowadays in practically all industrial and transportation sectors, for low‐voltage and medium‐voltage applications, and in a wide power range from fractional horsepower to multi‐megawatt rating.
This chapter mainly focuses on describing the most important and established control strategy for induction machines (i.e. the vector control). In this chapter, the motor side converter is supposed to be properly supplied, as represented in Fig. 2-1, by a DC supply source or grid converter.
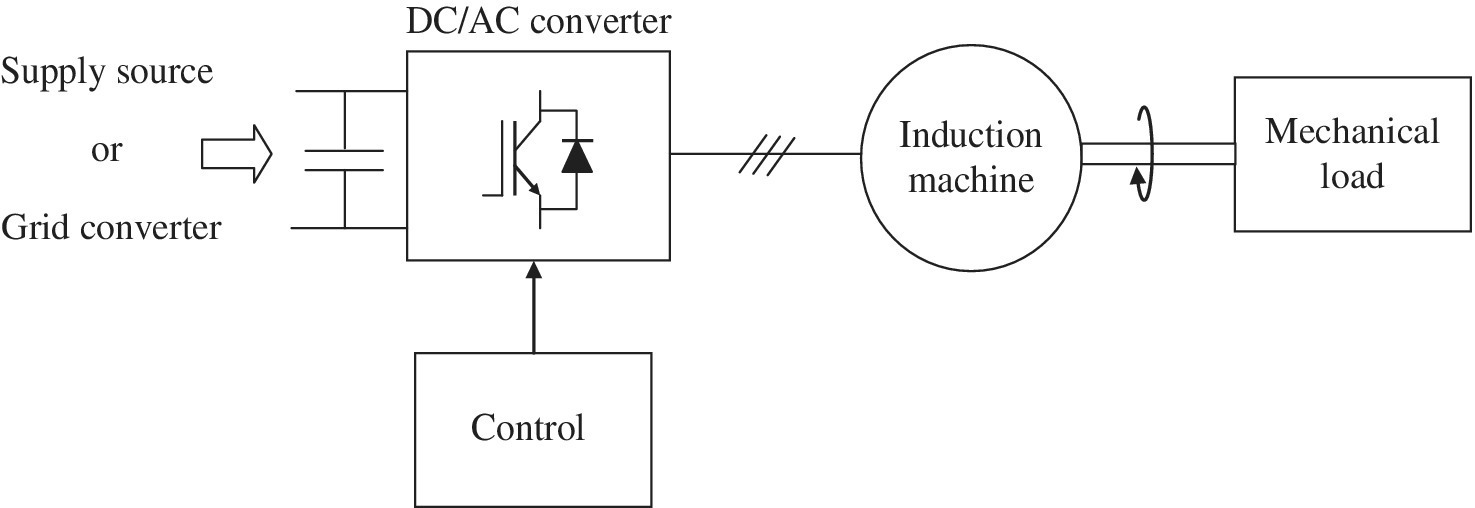
Fig. 2-1 Basic representation of motor side control of induction machine
Thus, in this chapter, first the modeling on the induction machine is studied, which later permits us to study and develop the core of the chapter: vector control strategies for induction machines. This control technique ...
Get Power Electronics and Electric Drives for Traction Applications now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

