October 2012
Intermediate to advanced
1152 pages
28h 19m
English
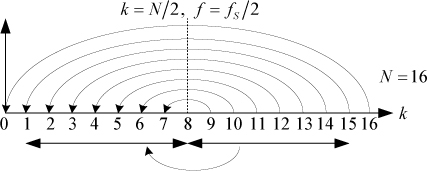
It is easy to mathematically represent an analog frequency on paper. The range of frequencies in the analog domain is both continuous and theoretically infinite. If we use the symbol fO to represent some arbitrary analog frequency all we need to do is to equate it with any one of an infinite number of available frequencies. We could, for example, choose fO to be equal to 23.456 Hz, or we could just as easily choose fO to be equal to 1.005 MHz. We could choose just about any other value to any precision that we can dream up. As long as we remain realistic, there is no limit on the values that fO can take ...