Chapter 3
Propagators and Second Quantization
The Schrödinger equation for an electron or for N noninteracting electrons is
![]()
with units such that Planck’s constant is 2π and the electron mass is 1, and with ξ = (![]() , ζ) being a combined space-spin variable. The wave function or Schrödinger amplitude
, ζ) being a combined space-spin variable. The wave function or Schrödinger amplitude ![]() (ξ, t) can be expressed in an orthonormal basis {us(ξ)} as
(ξ, t) can be expressed in an orthonormal basis {us(ξ)} as
![]()
giving the Schrödinger equation in discrete form
![]()
The notation
![]()
has been employed.
Let x be a unitary transformation to energy eigenstates: x†x = xx† = 1, x†hx = ∊ (diagonal). A formal solution to Eq. (3.3) may be written as
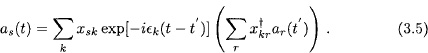
The system may be prepared such that |ar(t′)|2 = 1, and |as(t′)|2 = 0 for s ≠ r. Then the quantity
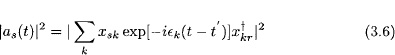
is the probability ...
Get Propagators in Quantum Chemistry, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

