February 2019
Beginner to intermediate
382 pages
10h 1m
English
Look at the following example, hyperplane C is the preferred one as it enables the maximum sum of the distance between the nearest data point in the positive side to itself and the distance between the nearest data point in the negative side to itself:
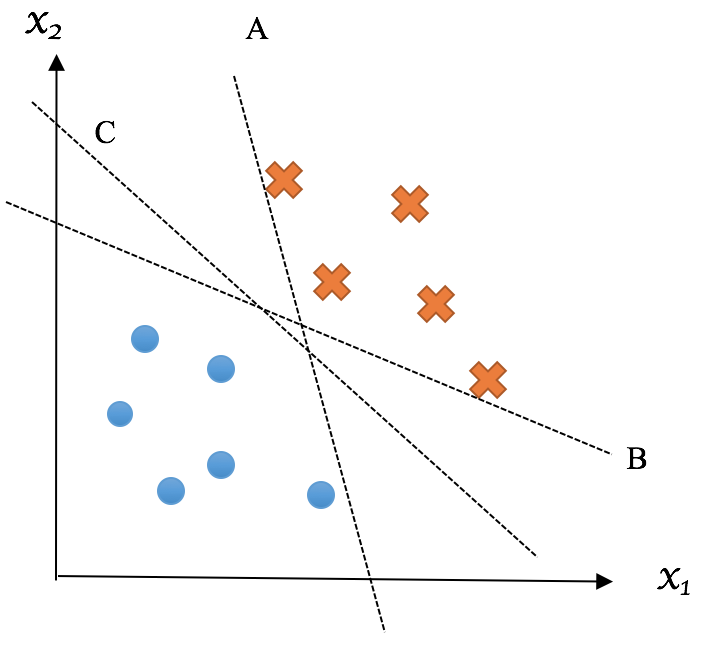
The nearest point(s) in the positive side can constitute a hyperplane parallel to the decision hyperplane, which we call a Positive hyperplane; on the other hand, the nearest point(s) in the negative side constitute the Negative hyperplane. The perpendicular distance between the positive and negative hyperplanes is called the Margin, whose value equates ...