SVM and many other classifiers can be applied to cases with more than two classes. There are two typical approaches we can take, one-vs-rest (also called one-versus-all), and one-vs-one.
In the one-vs-rest setting, for a K-class problem, it constructs K different binary SVM classifiers. For the kth classifier, it treats the kth class as the positive case and the remaining K-1 classes as the negative case as a whole; the hyperplane denoted as 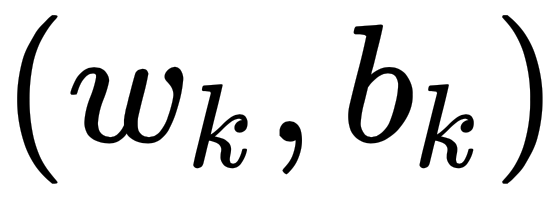 is trained to separate these two cases. To predict the class of a new sample, x', it compares the resulting predictions from K individual classifiers from ...
is trained to separate these two cases. To predict the class of a new sample, x', it compares the resulting predictions from K individual classifiers from ...

