11
QUANTUM CRYPTOGRAPHY
Secure communication can be accomplished through key distribution, a method by which two parties who want to communicate privately share a key that is used to encrypt or scramble a message. Later the key can be used to recover or decrypt the message. Currently cryptographic keys are generated using mathematical algorithms that are hard but not impossible to break. In contrast, quantum cryptography is a method of key distribution that relies on the laws of physics to create a key. While not 100% safe, quantum cryptography offers huge advantages over traditional methods.
Before we get into quantum cryptography, let’s look at a toy example to see how messages can be encrypted. Suppose that two parties, denoted Alice and Bob as usual, want to share a private message. A trivial way to encrypt the message is to generate a key k that is just a number used to scramble up the message. We can add k to each character in the message, for example, converting a useful message into a scrambled bunch of meaningless characters. Let’s say that we are representing the capital letters of the alphabet using a binary code. Since there are 26 letters in the alphabet, and 25 = 32, we need at least five bits to encode the alphabet using binary. If we start with the first four letters A, B, C, D as 0, 1, 2, 3, then we can encode the letters in the following way:
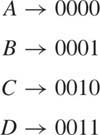
If we just transmitted ...