Sampling from distributions
Observing the outcome of trials that involve a random variable, a variable whose value changes due to chance, can be thought of as sampling from a probability distribution—one that describes the likelihood of each member of the sample space occurring.
That sentence probably sounds much scarier than it needs to be. Take a die roll for example.
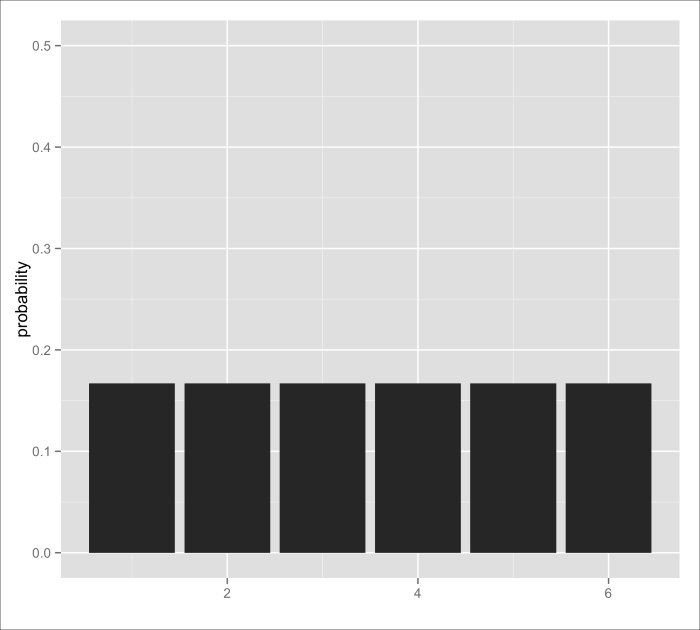
Figure 4.1: Probability distribution of outcomes of a die roll
Each roll of a die is like sampling from a discrete probability distribution for which each outcome in the sample space has a probability of 0.167 or 1/6. This is an example of a uniform distribution, because all the outcomes ...
Get R: Data Analysis and Visualization now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

