CHAPTER TEN
Oscillators and Harmonic Generators
10.1 OSCILLATOR FUNDAMENTALS
An oscillator is a circuit that converts energy from a power source (usually a dc power source) to ac energy. In order to produce a self-sustaining oscillation, there necessarily must be feedback from the output to the input, sufficient gain to overcome losses in the feedback path, and a resonator. There are a number of ways to classify oscillator circuits, one of those being the distinction between one-port and two-port oscillators. The one-port oscillator has a load and resonator with a negative resistance at the same port, while the two-port oscillator is loaded in some way at the two ports. In either case there must be a feedback path, although in the case of the one-port circuit this path might be internal to the device itself.
An amplifier with positive feedback is shown in Fig. 10.1. The output voltage of this amplifier is
![]()
which gives the closed-loop voltage gain
FIGURE 10.1 Circuit with positive feedback.
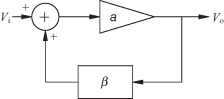
The positive feedback allows an increasing output voltage to feedback to the input side until the point is reached where
(10.2)
This is called the Barkhausen criterion for oscillation and is often ...

