CHAPTER SEVEN
Birefringence Control in Optical Fibers
7.1 PHYSICAL PARAMETERS FOR THE POLARIZATION CHARACTERIZATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS
In optics the direction of the electric field has a specific name, polarization. This might be confusing because the net electric dipole moment per unit volume, ![]() , bears the same name, polarization. In most cases, these two different physical quantities can be distinguished as “light polarization or equivalently electromagnetic wave polarization” and “electric polarization,
, bears the same name, polarization. In most cases, these two different physical quantities can be distinguished as “light polarization or equivalently electromagnetic wave polarization” and “electric polarization, ![]() .” In this chapter we will focus on the direction of electric field, the light polarization in optical fibers and the way to characterize its states, and finally methods to control its properties in optical fibers.
.” In this chapter we will focus on the direction of electric field, the light polarization in optical fibers and the way to characterize its states, and finally methods to control its properties in optical fibers.
Let us begin with basic nomenclature of polarization optics, assuming a monochromatic transverse electromagnetic wave propagating along z direction in vacuum. The electric field is confined in the x−y plane and its components can be described as
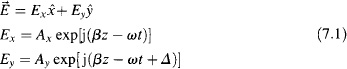
The phase retardance between Ex and Ey is denoted as Δ. And β is the propagation constant at the frequency of ω The locus of the electric field direction on the x−y plane, or equivalently polarization state, will be determined by ...
Get Silica Optical Fiber Technology for Devices and Components: Design, Fabrication, and International Standards now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

