Chapter 9
Energy Bands in Solids
9.1 INTRODUCTION
Isolated atoms have discrete energy levels. A familiar example is the hydrogen atom, first explained by Niels Bohr in 1913. The energy level diagram of a hydrogen atom has been shown in Figure 9.1.
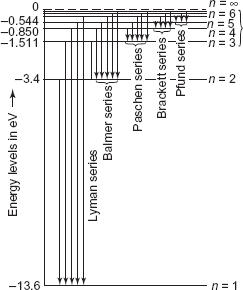
Figure 9.1 Energy level diagram of a hydrogen atom
When two atoms combine to form a diatomic molecule, each level of the individual atom is split into two close levels. If three atoms combine to form a triatomic molecule, each level of the isolated atom is split into three close levels. To make the picture clearer, energy levels of a hydrogen atom, a diatomic hydrogen molecule, and an imaginary ...
Get Solid State Physics now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

