16.3. Functions of Double Angles and Half-Angles
We come now to our last batch of identities, those involving two times an angle and those involving half an angle.
16.3.1. Functions of Double Angles
▪ Exploration:
Is the sine of twice an angle equal to twice the sine of that angle? Is sin 2α = 2 sin α? Try this: By calculator, evaluate
- sin 2(40°) 2 sin(40°)
Are these equal? Try it again with other angles. Try it for the cosine and tangent. What do you conclude?
NOTE
The sine of twice an angle is not twice the sine of the angle. Nor is the cosine (or tangent) of twice an angle equal to twice the cosine (or tangent) of that angle.
Remember to use the formulas from this section for all of the trig functions of double angles.
16.3.2. Sine of Twice an Angle
An equation for the sin 2α may be derived by setting β = α in the identity for sin(α + β).
- sin(α + α) = sin α cos α + cos α sin α
which we can rewrite as:
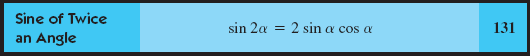
16.3.3. Cosine of Twice an Angle
Similarly, setting β = α in the identity for cos(α + β) gives
- cos(α + α) = cos α cos α − sin α sin α
which can also be written,
NOTE
![]()
There are two alternative forms to this identity. Since sin2α + cos2α = 1,
- cos2α = 1 − sin2α
Substituting yields
- cos 2α = 1 − sin2α − sin2α
Thus,
NOTE
Similarly, we can use the same identity, sin2α + cos
Get Technical Mathematics, Sixth Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

