6.1. PoC architecture
Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) PoC standard Release 1 architecture is based on PoC clients, PoC application server and PoC XML Document Management Server (XDMS). XDMS can be considered as a means of application configuration setting management as it stores application-specific configuration settings. An XDMS server that stores PoC-specific data is called a "PoC XDMS". Using reference point POC-8 (see Figure 6.3), the PoC server can fetch PoC-related documents (e.g., access lists) and using reference point POC-5 (see Figure 6.3), the PoC server can fetch generic lists (e.g., members of myfriends@example.com list) from a shared XDMS. The PoC servers handle application-specific tasks such as talk burst control (the reservation of talk burst for one user at a time) and PoC session control. They also provide interfaces to the operator's provisioning and network management systems and create application-specific Charging Detail Records (CDRs). The PoC server is connected to the IMS via the IMS Service Control reference point. The IMS takes care of common functions, such as user authentication for PoC, session routing and generic charging based on SIP. PoC client is usually software in the User Equipment (UE) but it could be an application (also in the PC).
Figure 6.1. Push to talk Over Cellular.
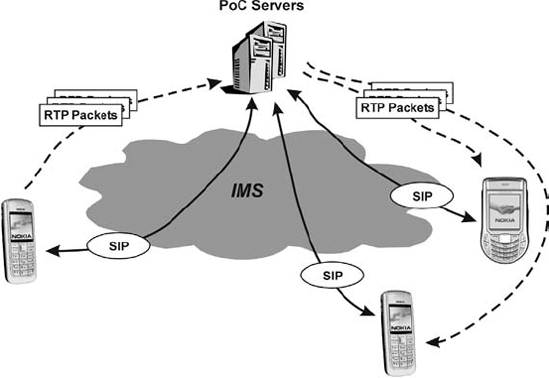
Figure 6.2. Voice call versus Push to talk Over Cellular.
Usually, ...
Get The IMS: IP Multimedia Concepts And Services, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

