4.9 Solutions of Large-Scale Electromagnetics Problems Involving PEC Objects
By developing and employing parallel implementations of MLFMA using the hierarchical partitioning strategy, electromagnetics problems discretized with hundreds of millions of unknowns can be solved both efficiently and accurately without resorting to approximation techniques. This section presents examples of numerical solutions of very large electromagnetics problems involving PEC objects with canonical and complicated geometries (see Figure 4.2). Since they are obtained by using a full-wave solver, numerical results presented in this section can be used for benchmarking purposes.
In all solutions presented in this section, the target accuracy is defined as maximum 1% error in far-zone electromagnetic fields. In order to achieve this error threshold with the best possible efficiency, some of the parameters can be listed as follows:
- Formulation: CFIE with
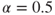 .
. - Discretization: Nearly equilateral triangles with edges smaller than
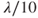 .
. - Near-Field Interactions: Adaptive integration methods with 0.5% maximumerror.
- Far-Field Interactions: Excess bandwidth formula with two digits of accuracy in the worst case.
- Interpolations/Anterpolations: Lagrange interpolation with stencils.
- Iterative Solutions: Convergence to 0.001 ...
Get The Multilevel Fast Multipole Algorithm (MLFMA) for Solving Large-Scale Computational Electromagnetics Problems now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

