Chapter 5
The Mechanics of Equity-Based Price Action
This chapter introduces the trader to the nuts and bolts of price and ratio valuation which are important considerations in the design of vibrational constructs. It covers simple profit and loss, market value, and leverage ratio calculations which form the basis for selecting the most appropriate ETF or CFD.
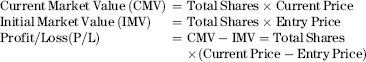
Equity-Based Calculations
Before we can grasp the finer points of vibrational trading, we need to be somewhat familiar with equity-based profit and loss calculations. Let's take a look at how to calculate the amount of gain or loss for every $1 move for a given number of shares.
Example 1
Assume that we are long 100 shares (one lot).
So, P/L for a $10 to $11 change in price is CMV − IMV:
![]()
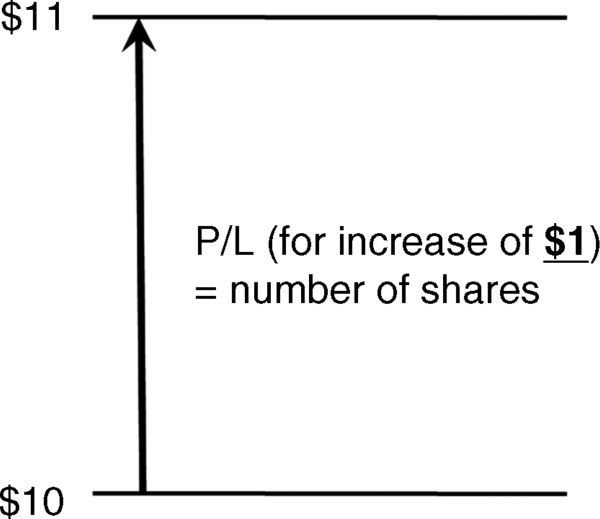
Therefore, the value of a dollar move is $100.
This happens to be the number of shares we are currently long (see Figure 5.1).
Figure 5.1 Measuring P/L
Example 2
Let us now assume that we are long 35 shares.
The P/L for an $11 to $10 drop in price is
![]()
Therefore, the value of a dollar move is −$35.
This again happens to be the number of shares ...

