Measuring Performances of a Classic LINQ Query
The goal of this paragraph is to explain how you can execute a classic LINQ query over intensive processing and measure its performance in milliseconds. Consider the following code:
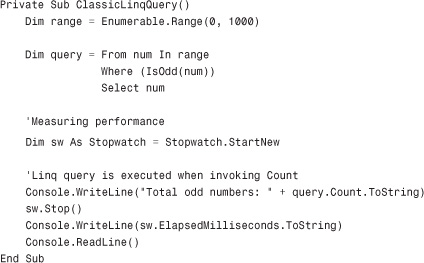
Given a range of predefined numbers (Enumerable.Range), the code looks for odd numbers and collects them into an IEnumerable(Of Integer). To measure performance, we can take advantage of the Stopwatch class that basically starts a counter (Stopwatch.StartNew). Because, as you already know, LINQ queries are effectively executed when you use them, such a query is executed when the code invokes the Count property to show ...
Get Visual Basic® 2010 Unleashed now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

