17.6 POWER ESTIMATION APPROACHES
Power estimation refers to the problem of estimating average power dissipation of digital circuits. Ideally the average power should include both the static and the dynamic power dissipations. However, for well-designed CMOS circuits, the capacitive power is dominant and therefore the average power generally refers to the capacitive power dissipation. This is much different from estimating the instantaneous or the worst-case power that is modeled as a voltage drop problem.
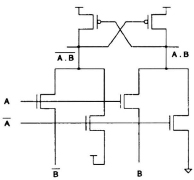
Fig. 17.16 Circuit realized using DC VS design style.
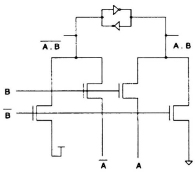
Fig. 17.17 Circuit realized using SRPL design style.
The design of low-power digital CMOS circuits cannot be achieved without accurate power prediction and optimization tools. Therefore, there is a critical need for CAD tools to estimate power dissipation during the design process to meet the power constraint without having to go through a costly redesign effort. The techniques for power estimation can be broadly classified into two categories: simulation based and nonsimulation based.
17.6.1 Simulation-Based Approaches
The main advantages of these techniques is that issues such as hazard generation, spatial/temporal correlation, etc. are automatically taken into account. The approaches under this category can be ...
Get VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

