8.5 CYCLIC CONVOLUTION
Cyclic convolution is also known as circular convolution. Let h = {h0, h1,· · ·, hn−1} be the filter coefficients and x = {x0,x1,· · ·,xn−1} be the data sequence. The cyclic convolution can be expressed as
![]()
and the output samples are given by
![]()
where ((i–k)) denotes (i–k) mod n. The cyclic convolution can be computed as a linear convolution reduced by modulo pn – 1. (Notice that there are 2n – 1 different output samples for this linear convolution). Alternatively, the cyclic convolution can be computed using CRT with m(p) = pn – 1, which is much simpler.
Example 8.5.1 Construct a 4 × 4 cyclic convolution algorithm using CRT with m(p) = p4 – 1 = (p – 1)(p + 1)(p2 + 1).
Solution
Let h(p) = h0 + h1p + h2p2 + h3p3 and x(p) = x0 + x1p + x2p2 + x3p3. Let m(0)(p) = p – 1, m(1)(p) = p + 1, m(2)(p) = p2 + 1. Let ![]() . Use the relationship (8.37) to construct the following table:
. Use the relationship (8.37) to construct the following table:
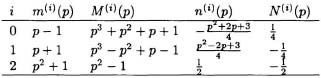
Compute residues
![]()
and
Notice that it takes 1 multiplication to compute and 1 to compute The computation ...
Get VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and Implementation now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

