6Mutual Authentication
6.1. 802.1x mechanism
The 802.1x access control mechanism is deployed in the Local Area Network (LAN) implementing the following technologies:
- – Ethernet technology in the case of access to a switch;
- – Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) in the case of a connection to an access point (AP).
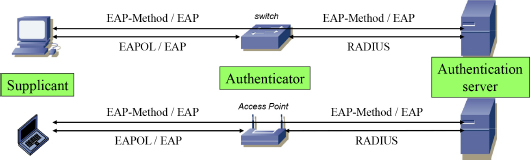
Figure 6.1. Components of 802.1x mechanism
The authentication uses the 802.1x access control mechanism that defines the following three components (Figure 6.1):
- – the supplicant is the device (network host) wishing to access the Ethernet or Wi-Fi network;
- – the authenticator is the device (Ethernet switch or Wi-Fi access point) that controls the supplicant’s access to the LAN;
- – the authentication server is the device that authenticates the supplicant and authorizes access to the LAN.
The 802.1x mechanism relies on the following set of protocols (Figure 6.2):
- – the extensible authentication protocol (EAP) over LAN (EAPOL), exchanged between the supplicant and the authenticator;
- – the EAP exchanged between the supplicant, on the one hand, and the authenticator or authentication server, on the other hand:
- - the EAP is carried by the EAPOL protocol on the interface between the supplicant and the authenticator;
- - the EAP carries EAP-Method messages exchanged between the supplicant and the authentication server;
- – the remote authentication dial-in user service (RADIUS) protocol, ...
Get Wi-Fi Integration to the 4G Mobile Network now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

