Chapter 3 The Nature of Equity Returns
Linkages: The Real Economy and the Financial Economy
Observers of the U.S. economy often draw a distinction between Main Street and Wall Street, as though the business and financial worlds operate in their own spheres. However, the real economy of Main Street—the production and consumption of goods and services—and the financial economy of Wall Street—the financial markets where stocks and bonds are traded—can be viewed as two sides of the same coin. Two important factors link the two aspects of the overall economy.
The sum of all goods and services produced in the real economy in a given year is measured by gross domestic product (GDP). Real GDP, which measures output in constant prices, emphasizes the growth in quantities produced, while nominal GDP adds in inflation, to take into account changes in both quantities and prices. The share of businesses’ profits in nominal GDP in the real economy, profit margins, corresponds to corporate earnings per share in the financial economy—the first important link (Figure 3.1).
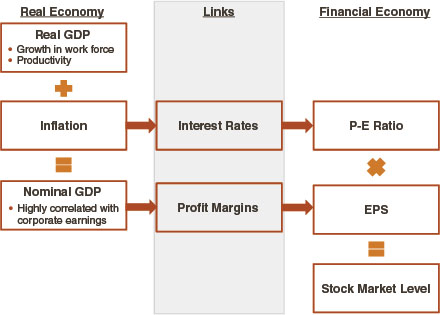
Figure 3.1 Links from the Real Economy to the Financial Economy
Sources: Crestmont Research; Epoch Investment Partners
The second key link between the real and financial economy is interest rates, which underlie the valuation of financial assets. Interest rates include a component to provide lenders with a real return ...
Get Winning at Active Management now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

