6.4 4G Standards and Systems
The first mobile telephony systems, based on a cellular network architecture, were deployed during the 1980s. These first systems, called 1G systems as an abbreviation to “first generation”, were based on analog FDMA technology, which could only support voice services. From there, and roughly every ten years, a new generation has been deployed to provide new and improved services. As such, the 1990s saw the deployment of 2G (second generation) systems, and 3G were deployed during the first decade of the 21st century. At the time of writing, 4G systems are starting to be deployed. Each generation of mobile telephony introduces new technological innovators aimed at improving the spectrum use efficiency, access latency, communication bit rate, reliability, etc. The 2G systems introduced the use of digital wireless technology in the form of time-division multiple access (TDMA) in the GSM standard or code-division multiple access (CDMA) in the IS-95 standard. Third generation systems are best exemplified by the UMTS standard, based on wideband-CDMA technology – see Figure 6.15.
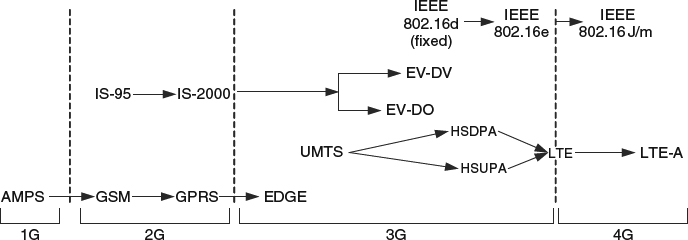
Figure 6.15 The evolution of cellular systems over different generations.
Regardless of the considered technology generation, a recurring and growing source of dissent is to what generation a standard belongs to. This has resulted in increasing lack of clarity, one that may be pointless ...
Get 3D Visual Communications now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

