TRADE LIFE CYCLE FOR FIXED INCOME SECURITIES—FAIR VALUE THROUGH PROFIT OR LOSS
- Buy the bond
- Accrued interest purchased
- Pay the contracted amount for the bond
- Coupon accrual
- Coupon receipt
- Reversal of accrued interest purchased
- Accrual of interest on valuation date
- Amortization of premium/discount on purchase
- Valuation of bond on valuation date
- Sell the bond (liquidation)
- Accrued interest on bond sold
- Receive the consideration
- Ascertain the profit/loss on the sale
- Fx revaluation entries
- Fx translation entries
Additional events in the trade life cycle
- Early redemption
- Maturity
- Write off
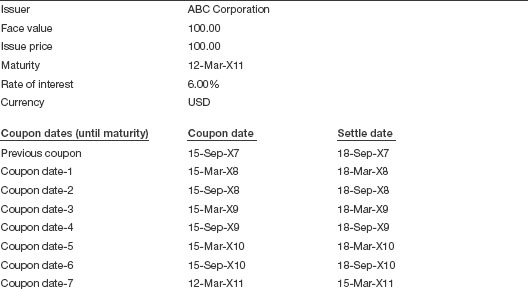
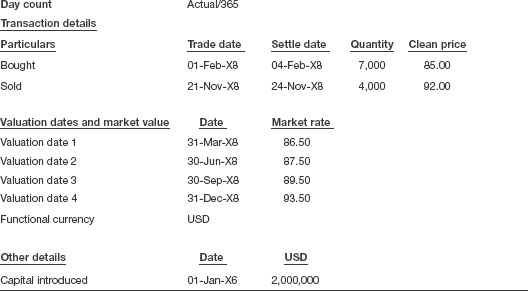
Let us assume the details as presented in Table 2.2 for the purpose of this illustration.
Table 2.2 Bond details
Buy the bond
Bonds are either subscribed at the initial offer through the primary market route or purchased through the secondary market. In a secondary market the buy order is placed through a broker known as counter party. Most corporate bonds are traded over-the-counter. If traded through the stock exchange, the concerned stock exchange usually takes the responsibility for specific performance of the contract ensuring that both legs of the contract are fulfilled by the respective parties. When an entity places the buy order and when the broker executes the same, it becomes a binding ...
Get Accounting for Investments, Volume 2: Fixed Income Securities and Interest Rate Derivatives—A Practitioner's Guide now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

