4.3 DIFAR Buoy Signal Processing
The DIFAR sensor (one of a class of vector sensors) is a passive receiver that operates on the broadband signal radiated from a distant ship and converts the signal into a noisy bearing to the ship using the process illustrated in Figure 4.4. The DIFAR buoy consists of three independent sensors: an omnidirectional hydrophone, an East–West dipole hydrophone, and a North–South dipole hydrophone. The dipole hydrophones may not line up in the proper orientation but their outputs are electronically mixed to produce two dipole outputs of the proper orientation. We will not discuss this reorientation process further because it is irrelevant to the tracking problem and we will always assume the output of each channel to be oriented with the Cartesian axes.
Figure 4.4 DIFAR sensor signal processing.
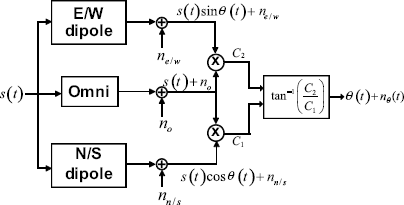
For simulation purposes, one needs to generate noisy bearing observations at the output of each simulated DIFAR sensor. From Figure 4.4 we see that for the m th sensor, the real signals output by each channel are given by
(4.10) ![]()
(4.11) ![]()
(4.12) ![]()
where s(t) represents ...
Get Bayesian Estimation and Tracking: A Practical Guide now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

