10.2 Two-Dimensional Spherical Simplex Sigma Points
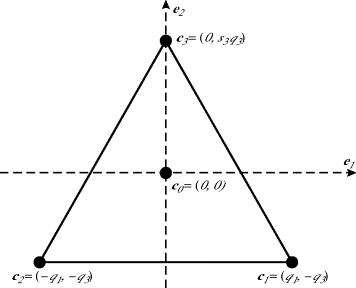
For the two-dimensional case, consider the vector points at the vertices of the simplex shown in Figure 10.1. In this equilateral triangle, all sides and angles are equal and all integration points are equidistant from the point at the origin. For this 2D case, the vector integration points are the set (c0, c1, c2, c3) = ![]() . Here, s3 is a scale factor that will be determined below.
. Here, s3 is a scale factor that will be determined below.
Figure 10.1 Depiction of a two-dimensional simplex with four vector integration points.
Once again, the moment equations (10.1)–(10.3) must be satisfied. Thus, from (10.1) it follows that
and (10.2) results in
Finally, (10.3) leads to
(10.20) ![]()
which reduces to the set of equations
(10.21) ![]()
From (10.18) it follows that
(10.23)
Get Bayesian Estimation and Tracking: A Practical Guide now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

