Chapter 9. Surfacing the Deep Web
What Is the Deep Web?
THE TERM "DEEP WEB" REFERS TO WEB CONTENT THAT LIES HIDDEN BEHIND HTML FORMS. IN ORDER to get to such content, a user has to perform a form submission with valid input values. Take, for example, the store locator form in Figure 9-1. Searching for stores in the zip code 94043 results in a web page with a listing of stores. The result page is an example of a web page in the Deep Web.
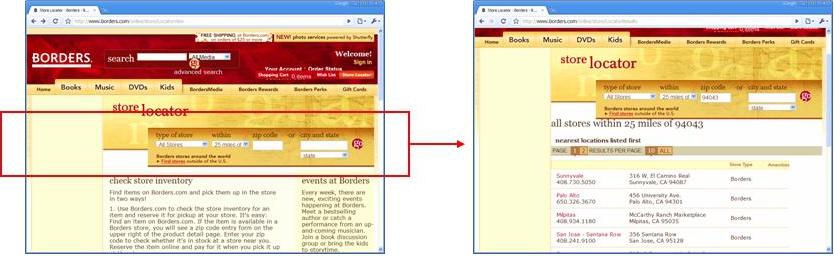
Figure 9-1. The Borders Store Locator form and a deep-web page resulting from a particular form submission. (See Color Plate 21.)
The Deep Web has been acknowledged as a significant gap in the coverage of search engines. This is because search engines employ web crawlers to discover web pages that will be included in their index, and traditionally these web crawlers were believed to rely exclusively on hyperlinks between web pages to discover new web content. They lacked the ability to automatically perform form submissions, and hence web pages behind forms were not included in the index of a search engine. The web page with the form typically carries very little information about the content of the pages behind the form; thus, common web users could get to Deep Web content only if they already knew of the existence of the corresponding HTML form or if search engines somehow led them to the form. They then had to perform the ...
Get Beautiful Data now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

