12
CALL FEATURES ON BONDS
The call feature on a bond gives the bond's issuer the right to force the bondholders to turn in their bonds for the call price. Call features are widely used for corporate and municipal government bonds.
The call price is the price paid to bondholders when the bond is called. It is par or above. Frequently, the call price starts out at par plus 1 year's interest. As the bond ages, the call price declines toward par (see Figure 12.1). The exact terms and dates are stated in the bond indenture.
In recent years, callable corporate bonds have had a period of call protection after the bond is originally issued. During the call-protected period, the bond cannot be called and replaced by another bond. However, most bonds can be called for reasons other than replacement with another, lower-cost bond – so-called redemptions. Thus, bonds can be redeemed and replaced by stock even during the period of call protection.
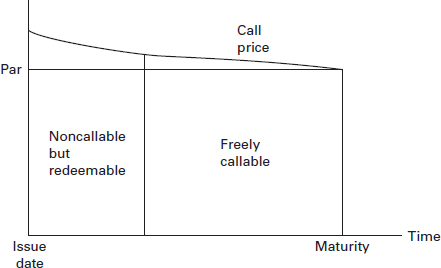
Figure 12.1 Features of callable bonds
Over time the proportion of corporate bonds containing call options has varied. At times, the large majority of bonds have had call features. At other times, the majority of bonds have been noncallable. When interest rates have been high, the proportion of callable bonds appears to have been relatively high, and when interest rates have fallen, the proportion of callable bonds has been relatively low.
Reasons for ...
Get Bonds and Bond Derivatives, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

