Application Architecture
The Application
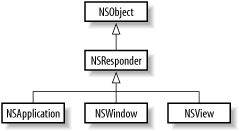
Kit’s basic architecture is primarily implemented in
three classes:
NSApplication
,
NSWindow
, and
NSView
. Figure 3-3 shows the
class hierarchy for these classes. Individually, these three classes
provide the means for an application to interface with the operating
system (and ultimately, the user) via connections to
Quartz, the window
server, and underlying Unix libraries through Core Foundation. Taken
as a whole, these classes form the backbone of the Application
Kit’s event-handling infrastructure.
 |
The Application
Fundamental to every Cocoa application is a singleton instance of
NSApplication (accessible by using the class
method sharedApplication or the global variable,
NSApp).
NSApplication
provides a link to the window server and
other essential operating system services. One of its most important
responsibilities is management of the application’s
run loop and event handling.
Run loops
have the job of managing input from sources such as the mouse and
keyboard (through the window server), ports, and timers. As the owner
of the application’s main run loop,
NSApplication is the first stop for event
processing in an application. Through a direct connection to the
window server, NSApplication accepts ...
Get Cocoa in a Nutshell now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

