Text System Architecture
The following four classes make up the core architecture of Cocoa’s text handling system:
NSTextStorageis the backbone data model responsible for storing text.NSTextViewis responsible for presentation in the view.NSLayoutManagerandNSTextContaineract as controllers between the model and the view.
The relationship between these core classes is based on the same Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern used throughout the Application Kit (and discussed in Chapter 3). Figure 5-2 shows the division of responsibilities in these four classes using the MVC pattern.
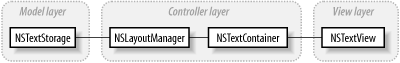 |
Figure 5-2 shows the relationship between the four
classes, but doesn’t show the one-to-many
relationship that may exist between instances of these classes.
Instances of NSTextStorage own and manage one or
more NSLayoutManager objects. Similarly, each
instance of NSLayoutManager owns one or more
NSTextContainer objects, while each text container
object is paired with an NSTextView object. The
nature of these relationships is what gives Cocoa’s
text handling system much of its flexibility and power.
NSTextView
NSTextView
represents the view, or
presentation, layer of the text system; it is the class that facilitates user interaction with the text system. User interaction consists of displaying text onscreen and ...
Get Cocoa in a Nutshell now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

