Turning the Transistor On
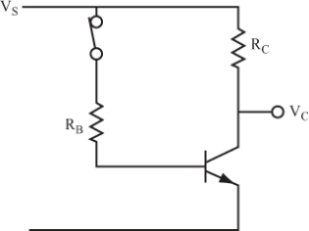
1 Start by examining how to turn a transistor ON by using the simple circuit shown in Figure 4.1. In Chapter 3, RB was given, and you had to find the value of collector current and voltages. Now, do the reverse. Start with the current through RC, and find the value of RB that turns the transistor ON and permits the collector current to flow.
Question
What current values do you need to know to find RB? _____
The base and collector currents
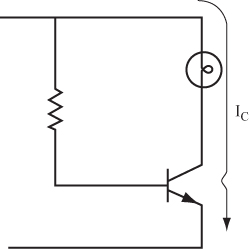
2 In this problem circuit, a lamp can be substituted for the collector resistor. In this case, RC (the resistance of the lamp) is referred to as the load, and IC (the current through the lamp) is called the load current.
3 For the transistor switch to perform effectively as a CLOSED switch, its collector voltage must be at the same voltage as its emitter voltage. In this condition, the transistor is said to be turned ON.
Get Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with Projects now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.