18.5 SMART CARDS
A smart card is a banking card containing an embedded processor; compared to a PC, the smart card's computational power and memory are significantly limited. The ISO standard 7810 specifies the physical details of the smart card designated as ID-1. The dimensions are 85.60 mm (L) × 53.98 mm (W) × 0.80 mm (T). Even the corner radius of 3.18 mm is specified. Leave nothing to chance!
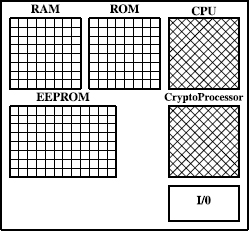
Figure 18.6 Smart card memory.
18.5.1 Smart Card Memory
Figure 18.6 illustrates the different types of memory contained on smart cards.
- ROM (read-only memory) – 6–24 Kbytes storing the operating system;
- RAM (random access memory) – 256–1024 bytes used as working memory; RAM is volatile, meaning that its contents are lost when power to the smart card is removed.
- EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable memory) – 1–16 Kbytes of memory that
- can be written to externally,
- can be erased externally by an electrical charge, and
- retains its state when the power is removed.
18.5.2 External Interface of Smart Cards
Most smart cards require an external source of energy. One standard method to transfer data is to use a card acceptor device (CAD), which allows for the half-duplex exchange of data at the rate of ≥9600 b/s. The ISO standard 7816/3 provides either six or eight connection points for (external) power to the smart card. ISO 7816, Part 1 [ISO, 1998] describes the locations and functions ...
Get Computer Security and Cryptography now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

