Chapter 5. Queues
A queue is a type of list where data are inserted at the end and are removed from the front. Queues are used to store data in the order in which they occur, as opposed to a stack, in which the last piece of data entered is the first element used for processing. Think of a queue like the line at your bank, where the first person into the line is the first person served, and as more customers enter a line, they wait in the back until it is their turn to be served.
A queue is an example of a first-in, first-out (FIFO) data structure. Queues are used to order processes submitted to an operating system or a print spooler, and simulation applications use queues to model scenarios such as customers standing in the line at a bank or a grocery store.
Queue Operations
The two primary operations involving queues are inserting a new element into a queue and removing an element from a queue. The insertion operation is called enqueue, and the removal operation is called dequeue. The enqueue operation inserts a new element at the end of a queue, and the dequeue operation removes an element from the front of a queue. Figure 5-1 illustrates these operations.
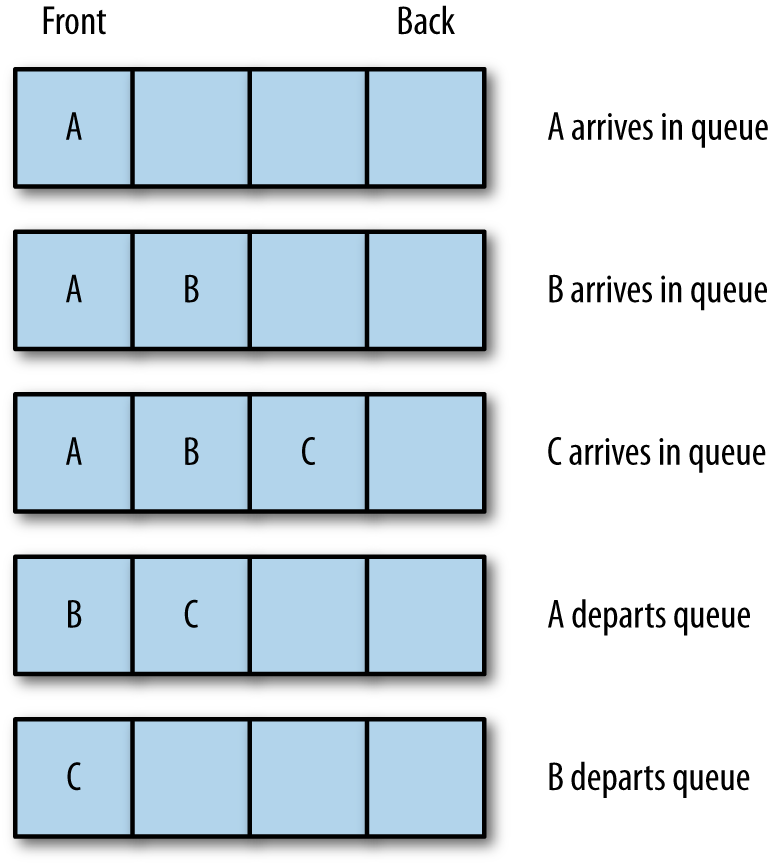
Figure 5-1. Inserting and removing elements from a queue
Another important queue operation is viewing the element at the front of a queue. This operation is called peek. The peek operation returns the element stored at ...
Get Data Structures and Algorithms with JavaScript now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

