Schematics
A major problem common in utilizing a microcontroller in a mixed-signal environment (one that combines both digital and analog components) is the noise the digital subsystem introduces. Higher processor performance normally results in greater noise in the analog section, unless great pains are undertaken to minimize these effects. Thus, achieving high throughput is often contrary to the goal of keeping the analog circuits as noise-free as possible. The MAXQ implements intelligent clock management that reduces noise by enabling clocks only to those subsystems that require them, and only when they require them. In this way, the overall digital noise is reduced considerably. The MAXQ processor requires two crystals, a 16 MHz crystal (X1) for the main CPU clock and a 32.768 kHz watch crystal (X2) for the timers. Figure 17-2 shows the MAXQ2000F processor with its support components.
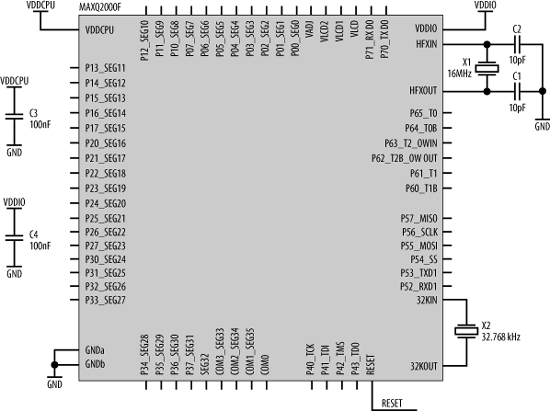
Figure 17-2. MAXQ processor and support components
The MAXQ processor requires two power supplies, VDDCPU (2.5 V) and VDDIO (3.6 V), each decoupled to ground with 100 nF ceramic capacitors. The 2.5 V supply may be generated using a MAX1658 (Figure 17-3). This is a general-purpose regulator, the output of which is adjustable via bias resistors. These resistors, R1 and R2, set the output to +2.5 V. It is important that these resistors are precise, so choose resistors with 1% tolerance. The input ...
Get Designing Embedded Hardware, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

