Chapter 8. Multicasting: Using MADCAP
With the introduction of Windows 2000, Microsoft added a number of advanced features to the DHCP Server. Many of these features have been discussed in earlier chapters. The new DHCP Server in Windows 2000 also includes the ability to automatically assign multicast IP addresses to DHCP clients. This chapter is dedicated to discussing multicast address allocation via DHCP.
Multicast Address Allocation
Administrators can benefit from having a service, much like DHCP, that automatically assigns multicast addresses to clients. This new service is known as Multicast Address Dynamic Client Allocation Protocol (MADCAP). MADCAP is currently defined in RFC2730 (http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2730.txt).
But before I dive into MADCAP, let’s take a moment to define what multicasting is.
Most communication that occurs on a network is in the form of unicast messages. A unicast message is a single point-to-point message between a sender and a receiver (see Figure 8.1). TCP and UDP use this method of communication.
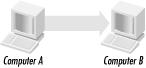
Figure 8-1. Unicasting
Another type of message is the broadcast message. A broadcast message is sent from a sender to all computers on the network (see Figure 8.2). As noted in earlier chapters, DHCP relies on this form of communication.
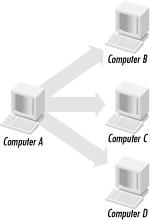
Figure 8-2. Broadcasting ...
Get DHCP for Windows 2000 now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

