Chapter 2
Quantization
Basic operations for AD conversion of a continuous-time signal x(t) are the sampling and quantization of x(n) yielding the quantized sequence xQ(n) (see Fig. 2.1). Before discussing AD/DA conversion techniques and the choice of the sampling frequency fS = 1/TS in Chapter 3 we will introduce the quantization of the samples x(n) with finite number of bits. The digitization of a sampled signal with continuous amplitude is called quantization. The effects of quantization starting with the classical quantization model are discussed in Section 2.1. In Section 2.2 dither techniques are presented which, for low-level signals, linearize the process of quantization. In Section 2.3 spectral shaping of quantization errors is described. Section 2.4 deals with number representation for digital audio signals and their effects on algorithms.
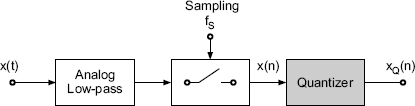
Figure 2.1 AD conversion and quantization.
2.1 Signal Quantization
2.1.1 Classical Quantization Model
Quantization is described by Widrow's quantization theorem [Wid61]. This says that a quantizer can be modeled (see Fig. 2.2) as the addition of a uniform distributed random signal e(n) to the original signal x(n) (see Fig. 2.2, [Wid61]). This additive model,
![]()
is based on the difference between quantized output and input according to the ...
Get Digital Audio Signal Processing, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

