Chapter 8
Sampling Rate Conversion
Several different sampling rates are established for digital audio applications. For broadcasting, professional and consumer audio, sampling rates of 32, 48 and 44.1 kHz are used. Moreover, other sampling rates are derived from different frame rates for film and video. In connecting systems with different uncoupled sampling rates, there is a need for sampling rate conversion. In this chapter, synchronous sampling rate conversion with rational factor L/M for coupled clock rates and asynchronous sampling rate conversion will be discussed where the different sampling rates are not synchronized with each other.
8.1 Basics
Sampling rate conversion consists out of upsampling and downsampling and anti-imaging and anti-aliasing filtering [Cro83, Vai93, Fli00, Opp99]. The discrete-time Fourier transform of the sampled signal x(n) with sampling frequency fS = 1/T (ΩS = 2πfS) is given by
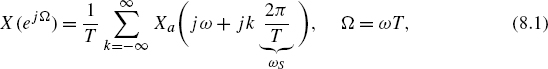
with the Fourier transform Xa(jΩ) of the continuous-time signal x(t). For ideal sampling the condition
![]()
holds.
8.1.1 Upsampling and Anti-imaging Filtering
For upsampling the signal
![]()
by a factor L between consecutive samples L − 1 zero samples will be included (see Fig. 8.1). ...
Get Digital Audio Signal Processing, Second Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

