CHAPTER 5DAUBECHIES WAVELET TRANSFORMATIONS
The discrete Haar wavelet transformation introduced in Chapter 4 serves as an excellent introduction to the theory and construction of orthogonal wavelet transformations. We were able to see in Section 4.4 how the wavelet transformation can be utilized in applications such as image compression and edge detection. There are advantages and limitations to the Haar wavelet transformation. Conceptually, the Haar wavelet transformation is easy to understand. The big advantage of the Haar wavelet transformation is computational speed. Each row of the Haar wavelet transformation matrix consists of only two nonzero terms so it straightforward to write fast algorithms to apply the transformation to a vector or matrix. This same advantage is also a disadvantage. Consider the vector v ∈ ℝ40 where
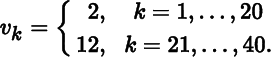
The vector v and its Haar wavelet transformation are plotted in Figure 5.1.
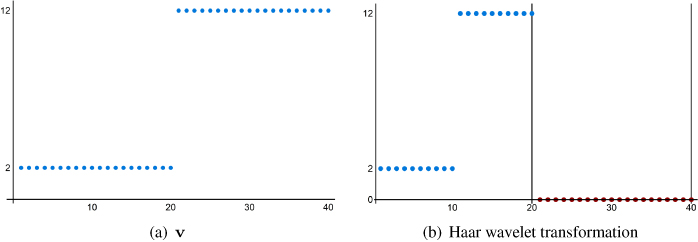
Figure 5.1 A vector and its Haar wavelet transformation.
Recall in Section 4.4 we searched for edges in images by replacing the blur of the transformation with a zero matrix and then inverting the modified transformation. We could certainly do the same for vectors but in this case, if we set the values of the averages portion to 0, then the modified transformation vector is the zero ...
Get Discrete Wavelet Transformations, 2nd Edition now with the O’Reilly learning platform.
O’Reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.

